一、组件化 1.目的 为了解耦:把复杂系统拆分成多个组件,分离组件边界和责任,便于独立升级和维护。
2.好处
按合理的粒度将系统拆分成多个组件,确保组件各司其职,以便于复用。
开发人员只须关注自己的组件,不再需要导入或编译其他组件,从而提升开发和编译速度。
通信层实现了组件间的通信,而不用在组件间跳转、调用服务时引用其他组件的文件。
3.方案 目前 iOS 组件化的实践中,比较流行的解决方案可归纳为以下三种:
1.基于URL+Block的路由方案;
2.基于反射原理的方案;
3.面向协议的注册服务方案;
“没有最优的方案,只有更适合自己的方案”。
三种方案各有优缺点。你可只选其一,也可将它们组合起来使用。前提是要理解所选方案的特点,结合项目的实际需求进行取舍。
接下来的文章中,将陆续对这三种方案进行分析和梳理~
二、URL路由方案 1.场景 从主页跳转到详情,传入详情页所需的头像;
在详情中简单的修改信息之后,返回主页时更新主页的标题。
2.思路 这是一个简单的组件间页面跳转服务,在组件化之前,我们最常见的处理可能是:
在主页中引用详情的.h头文件;
创建详情的实例;
通过详情提供的接口传入图片;
将主页设置为详情的代理;
push到详情页。
这种处理的问题在于:主页中依赖了详情的头文件,且直接持有了详情的实例;详情的delegate反过来持有了主页的实例,这样两个模块间就产生了依赖和耦合。这还只是主页到详情的一种情况,如果有其他模块同样需要跳转详情,则这些模块同样也会与详情之间产生耦合。
组件化的实践中,按照合理的粒度将系统划分为多个组件之后,主要的挑战就变成了如何实现各组件之间的通信,同时减少组件间的耦合。
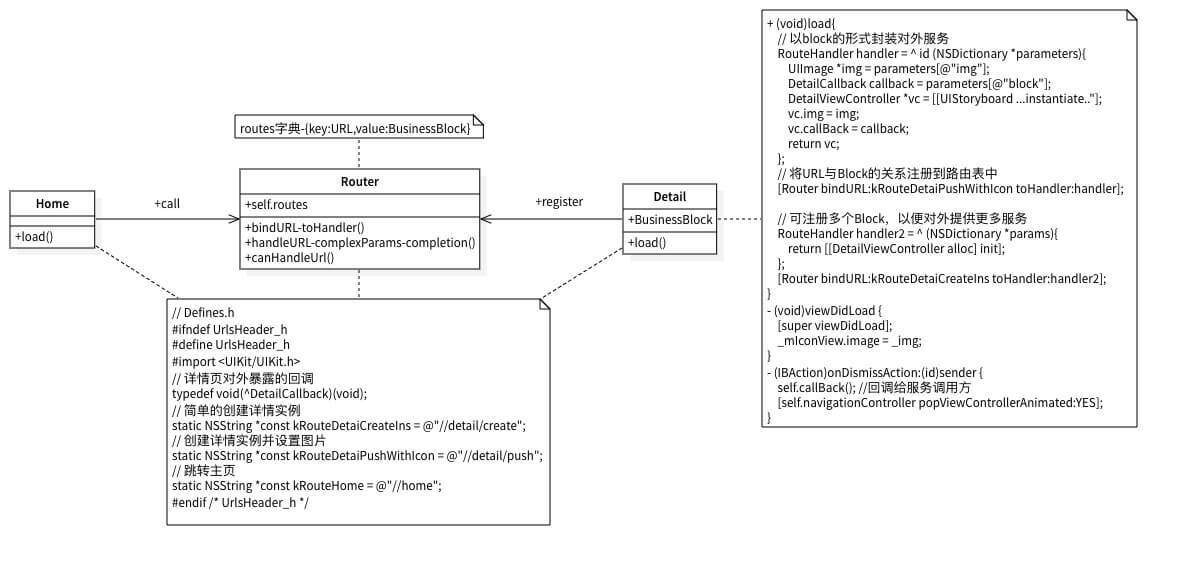
针对这一问题,URL+Block路由方案的实现思路和原理如下:
2.1.服务Block 将创建详情实例的服务封装成一个block:
1 2 3 4 return [[DetailViewController alloc] init ];
2.2.服务URL 定义URL,用它表示详情组件中的某项服务:
1 2 3 4 5 static NSString *const kRouteDetaiCreateIns = @"//detail/create" ;static NSString *const kRouteDetaiPushWithIcon = @"//detail/push" ;
2.3.映射URL与Block 在单例类Router中将表示某项服务的URL与真正封装了服务的Block映射到字典中:
1 [Router bindURL:kRouteDetaiPushWithIcon toHandler:handler]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void )bindURL:(NSString *)urlStr toHandler:(RouteHandler)handler{self .routes setValue:handler forKey:urlStr];NSMutableDictionary *)routes {@synchronized (self ) {static NSMutableDictionary *_routes = nil ;if (!_routes) {NSMutableDictionary dictionary];return _routes;
2.4.调用服务 在主页中通过Router调用详情的服务并获取返回值:
1 2 3 4 UIViewController *vc = [Router handleURL:url complexParams:params completion:^(id result) {self .title = @"Updated" ;self .navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES ];
2.5.服务路由查询 +handleURL接口内部会根据之前保存的URL-Block映射关系,以url为key去查询对应的Block并执行它:
1 2 3 + (nullable RouteHandler)handlerForURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {return [self .routes valueForKey:urlStr];
3.示例 3.1.映射URL与服务 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #ifndef UrlsHeader_h #define UrlsHeader_h #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> typedef void (^DetailCallback)(void );static NSString *const kRouteDetaiCreateIns = @"//detail/create" ;static NSString *const kRouteDetaiPushWithIcon = @"//detail/push" ;static NSString *const kRouteHome = @"//home" ;#endif
Defines.h头文件用于定义URL,也包括其他必要参数。它是一个通用文件,不属于某个组件,可在.pch文件中导入此头文件。
在这里你可以定义一个URL字符串@"//detail/push,其中第一个字符串”detail”表示详情组件,第二个字符串”push“表示跳转功能。后面我们就使用此URL来实现从主页到详情的跳转。
3.2.定义Router 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 typedef _Nullable id (^RouteHandler)( NSDictionary * _Nullable parameters);typedef void (^RouteCompletion)(_Nullable id result);@interface Router : NSObject void )bindURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr nonnull RouteHandler)handler;nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStrnullable NSDictionary *)complexParamsnullable RouteCompletion)completion;BOOL )canHandleUrl:(NSString *)urlStr;@end #import "Router.h" static Router *mInstance = nil ;@implementation Router instancetype )sharedInstance{return [[self alloc] init];instancetype )allocWithZone:(struct _NSZone *)zone{static dispatch_once_t onceToken;dispatch_once (&onceToken, ^{super allocWithZone:zone];return mInstance;NSMutableDictionary *)routes {@synchronized (self ) {static NSMutableDictionary *_routes = nil ;if (!_routes) {NSMutableDictionary dictionary];return _routes;void )bindURL:(NSString *)urlStr toHandler:(RouteHandler)handler{self .routes setValue:handler forKey:urlStr];nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStrnullable NSDictionary *)complexParamsnullable RouteCompletion)completion {NSString *URLKey = [self getKeyFromURL:urlStr];self handlerForURL:URLKey];NSDictionary *paramsInURL = [self .class parametersInURL:urlStr];NSMutableDictionary *params = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithDictionary:complexParams];id obj = handler(params);return obj;nullable NSDictionary *)parametersInURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {NSURL *URL = [NSURL URLWithString:urlStr];NSMutableDictionary *params = nil ;NSString *query = URL.query;if (query.length > 0 ) {NSMutableDictionary dictionary];NSArray *list = [query componentsSeparatedByString:@"&" ];for (NSString *param in list) {NSArray *elts = [param componentsSeparatedByString:@"=" ];if ([elts count] < 2 ) continue ;NSString *decodedStr = [[elts lastObject] stringByRemovingPercentEncoding];return params;nullable RouteHandler)handlerForURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {return [self .routes valueForKey:urlStr];BOOL )canHandleUrl:(NSString *)urlStr{return [self getKeyFromURL:urlStr].length != 0 ;NSString *)getKeyFromURL:(NSString *)urlStr{NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlStr];NSString *host = url.host;NSString *path = url.path;NSString *URLKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"//%@%@" ,host,path];return URLKey;@end
这是URL路由方案中的核心类。其主要作用有:
提供全局静态字典,以便保存URL与Block的映射关系;
提供接口以便调用方通过约定好的URL调用目标组件的服务;
一些需要注意的细节:
1、+bindURL接口中的urlStr参数是代表目标组件服务接口的纯URL,如"//detail/push",不带任何其他参数,在全局字典中保存映射关系时,key=URL,value=block。
2、+handleURL接口中的urlStr参数则是完整的URL,可包含调用方向目标组件传递的参数,如”//detail/push?a=1&b=1”;
3、在+handleURL方法内根据URL查询Block时,key为从urlStr中拆分出的url.host+url.path部分,即“//detail/push”;
4、本示例中Router.h只提供了最简单和最主要的两个接口,实际使用中可根据需求自己扩展其他功能,这里不做过多的延伸,因为后面会讲到有赞开源的库Bifrost,那里进行了完善的封装。
3.3.注册服务 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 @interface DetailViewController : UIViewController @property (nonatomic , strong ) UIImage *img;@property (nonatomic , copy ) DetailCallback callBack; @end #import "Router.h" @interface DetailViewController ()@property (weak , nonatomic ) IBOutlet UIImageView *mIconView;@end @implementation DetailViewController void )load{id (NSDictionary *parameters){UIImage *img = parameters[@"img" ];@"block" ];UIStoryboard storyboardWithName:@"Main" bundle:nil ]@"DetailViewController" ];return vc;NSDictionary *params){return [[DetailViewController alloc] init];void )viewDidLoad {super viewDidLoad];IBAction )onDismissAction:(id )sender {self .callBack(); self .navigationController popViewControllerAnimated:YES ];void )dealloc{NSLog (@"+++DetailViewController dealloced~~" );@end
这一步是在被调用的组件中进行的,即DetailViewController。注册的操作是在+load()方法中进行的,这样就能保证在应用启动阶段将表示当前组件服务接口的URL和block自动注册到Router中,以便后面随时调用。
+load()方法中可以注册多个对外提供服务的block,就相当于对外提供了多个接口,区分好对应的URL即可。
3.4.本地调用服务 所谓本地调用,就是我们的应用内部组件之间的服务调用,比如主页调用详情的接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #import "Router.h" @implementation HomeViewController void )viewDidLoad {super viewDidLoad];IBAction )onPushAction:(id )sender {self .title = @"Info Checked" ;NSDictionary *params = @{@"img" :[UIImage imageNamed:@"1" ],@"block" :block};NSString *url = [kRouteDetaiPushWithIcon stringByAppendingString:@"?num=1&orderid=10001" ];UIViewController *vc = [Router handleURL:url complexParams:params completion:^(id result) {self .title = @"Updated" ;self .navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES ];@end
调用方使用约定好的URL字符串指明要调用的服务接口;
将简单的参数以URL.query的形式拼接到URL中;
对于复杂的参数,可包装到字典params中;
回调函数中定义好自己的业务逻辑,作为completion参数;
通过Router调用服务,传入之前的参数,等待接收并处理返回值即可。
3.5.远程服务调用 所谓远程调用,就是别的应用向我们的应用发起的服务调用,大致过程如下:
别的应用通过[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:url]传递指定格式的URL到我们的应用;
我们的应用在下面的回调中接收URL,经过Router查询和调用与URL绑定的服务Block:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 - (BOOL )application:(UIApplication *)app NSURL *)url NSDictionary <UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey ,id > *)optionsBOOL canHandle = [Router canHandleUrl:url.absoluteString];if (canHandle) {nil completion:^(id result) {return canHandle;
远程调用时传递的URL一定要按照约定的格式拼接;
基于URL的远程调用有个缺点,即URL中参数的类型将会受到限制,图片、数据、block等类型的参数将无法直接拼接到URL后面。
4.流程总结
将组件对外提供的服务以Block的形式进行封装;
定义URL以表示组件对外提供的某个接口;
应用启动阶段在全局字典中保存URL与Block的映射关系;
简单参数拼接到URL中,复杂参数包装到complexParams字典中;
服务调用方传入URL,由Router查询并调用与之绑定的Block;
5.目录结构 整个工程的目录结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 ..h .m .xcassets .appiconset .json .lproj .storyboard .storyboard .h .pch .h .m .h .m 1 @2 x.png 1 @3 x.png .plist .h .m main .m
6.Bifrost 整个URL解耦方案的核心是Router类:
提供注册接口,将URL与Block的映射关系保存到全局字典中;
根据URL查询并调用对应Block。
这里着重推荐一下有赞开源的组件化库”#Bifrost“ ,它提供了对Router完善的封装。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 #import "Bifrost.h" #define BFComplete(Params, Result) [Bifrost completeWithParameters:Params result:Result] extern NSString * _Nonnull const kBifrostRouteURL; extern NSString * _Nonnull const kBifrostRouteCompletion; typedef _Nullable id (^BifrostRouteHandler)( NSDictionary * _Nullable parameters);typedef void (^BifrostRouteCompletion)(_Nullable id result);@interface Bifrost (Router )void )bindURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr toHandler:(nonnull BifrostRouteHandler)handler;void )unbindURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr;void )unbindAllURLs;BOOL )canHandleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr;nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr;nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStrnullable BifrostRouteCompletion)completion;nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStrnullable NSDictionary *)complexParamsnullable BifrostRouteCompletion)completion;void )completeWithParameters:(nullable NSDictionary *)params result:(_Nullable id )result;@end
从头文件中可以看到,Bifrost的主要功能包括:
绑定URL-Block;
根据URL处理简单参数、复杂参数、带回调的服务调用;
解除单个或所有URL与Block的映射;
检测某个URL是否绑定了Block;
具体的实现代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 #import "Bifrost+Router.h" #define BFLog(msg) NSLog(@"[Bifrost] %@" , (msg)) #define BFKey(URL) [Bifrost keyForURL:URL] NSString *const kBifrostRouteURL = @"kBifrostRouteURL" ;NSString *const kBifrostRouteCompletion = @"kBifrostRouteCompletion" ;@implementation Bifrost (Router )nonnull NSString *)keyForURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {NSURL *URL = [NSURL URLWithString:urlStr];NSString *key = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@%@" , URL.host, URL.path];return key;nullable NSDictionary *)parametersInURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {NSURL *URL = [NSURL URLWithString:urlStr];NSMutableDictionary *params = nil ;NSString *query = URL.query;if (query.length > 0 ) {NSMutableDictionary dictionary];NSArray *list = [query componentsSeparatedByString:@"&" ];for (NSString *param in list) {NSArray *elts = [param componentsSeparatedByString:@"=" ];if ([elts count] < 2 ) continue ;NSString *decodedStr = [[elts lastObject] stringByRemovingPercentEncoding];return params;NSMutableDictionary *)routes {@synchronized (self ) {static NSMutableDictionary *_routes = nil ;if (!_routes) {NSMutableDictionary dictionary];return _routes;void )bindURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr toHandler:(nonnull BifrostRouteHandler)handler {self .routes setObject:handler forKey:BFKey(urlStr)];void )unbindURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {self .routes removeObjectForKey:BFKey(urlStr)];void )unbindAllURLs {self .routes removeAllObjects];nullable BifrostRouteHandler)handlerForURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {return [self .routes objectForKey:BFKey(urlStr)];BOOL )canHandleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {if (urlStr.length == 0 ) {return NO ;if ([self handlerForURL:urlStr]) {return YES ;else {return NO ;nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStr {return [self handleURL:urlStr complexParams:nil completion:nil ];nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStrnullable BifrostRouteCompletion)completion {return [self handleURL:urlStr complexParams:nil completion:completion];nullable id )handleURL:(nonnull NSString *)urlStrnullable NSDictionary *)complexParamsnullable BifrostRouteCompletion)completion {id obj = nil ;@try {self handlerForURL:urlStr];NSMutableDictionary *params = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithDictionary:complexParams];self .class parametersInURL:urlStr]];if (completion) {if (!handler) {NSString *reason = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Cannot find handler for route url %@" , urlStr];NSMutableDictionary *userInfo = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];NSException *exception = [[NSException alloc] initWithName:BifrostExceptionNameself getExceptionHandler];if (handler) {else {@catch (NSException *exception) {NSMutableDictionary *userInfo = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithDictionary:exception.userInfo];NSException *ex = [[NSException alloc] initWithName:exception.nameself getExceptionHandler];if (handler) {@finally {return obj;void )completeWithParameters:(nullable NSDictionary *)params result:(_Nullable id )result {if (completion) {@end
库的实现并不复杂,各接口的作用已经在上面标明。它提供了异常情况的报错,同时URL和参数的处理也值得借鉴。
7.方案评价 无论是我们自己的Router还是有赞的Bifrost,其实现组件化的思路都是一样的:都是URL与Block的绑定和路由。
优点:
巧妙的利用了URL的通用性,支持多端统一跳转;
在应用启动阶段即完URL与成服务block的绑定;
组件之间通过Router进行通信,不再需要引用对方的头文件;
缺点:
远程调用时,只支持简单参数;
本地调用时,传递复杂参数只能包装到complexParams字典中,不够灵活;
组件间需要传递实体数据时,还需要导入对方的实体头文件,还是有依赖。
综合来看,在进行组件化时,基于URL-Block的路由方案只适合用来进行简单的本地和远程界面跳转,但其Router路由的思路是值得借鉴的。下一篇将继续介绍基于反射原理的组件化方案~
相关参考:
#©URL+Block方案demo
#©反射方案demo
#©服务协议注册方案demo
#©有赞Bifrost